Describe a System Buffered With Carbonic Acid
Carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system converts. The carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system plays an extremely important role in maintaining pH homeostasis of the blood.

Rest 2210 Ch End Of 6 And 7 Co2 Transport Flashcards Quizlet
Protein buffer systems work predominantly inside cells.
. PH 74 is11 pH units away from the pK so you would be on the edge of carbonic acids buffering capability. A buffer of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and bicarbonate HCO 3 is needed in blood plasma to maintain a pH between 735 and 745. In blood plasma the carbonic acid and hydrogen carbonate ion equilibrium buffers the pH.
Carbonic acid is already a component of the buffering system of blood. Acid-Base Balance CO2HCO3- is the most important physiological buffer system in the body. In contrast when the blood pH decreases ie becomes more acidic from the addition of a strong acid the equilibrium moves to the left.
Bicarbonate buffer system is the acid base homeostatic mechanism which includes balance of following. Protons or hydrogen ions are what determine the pH of the. In this buffer hydronium and bicarbonate anion are in equilibrium with carbonic acid.
The Carbonic Acid System. The effects of ear canal acoustics on hearing ability. A right shift forces more carbonic acid to dissociate which in turn causes the pH to decrease.
The bicarbonate buffer system works in the body because carbonic acid and the bicarbonate ion work together to gain or lose protons. This buffer system is physiologically most important because of its quantitative capacity to buffer acid or alkali loads and because of the capacity for independent regulation of HCO 3 and P CO2 by the kidneys and lungs respectively. Buffer systems are made of either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt.
A buffer is used to resist. The buffer systems functioning in blood plasma include plasma proteins phosphate and bicarbonate and carbonic acid buffers. When significant amounts of both carbonic acid and bicarbonate are present a buffer is formed.
Carbonic acid bicarbonate buffer system. In short H 2 PO 4 1- H HPO 4 2- In which H 2 PO 4 1- is the weak acid and HPO 4 2- is the base The phosphate buffer system happens in the kidney tubules where PO 4 3 is found. Please describe the biochemical processes involving hemoglobin and carbonic acid buffer system when blood pH drops.
Higher amounts of CO 2 in blood will drive the formation of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 which lowers the pH of the blood creating a more acidic environment. Industrially buffer solutions are used in fermentation processes and in setting the correct conditions for dyes used in coloring fabrics. To understand how the carbonic-acid bicarbonate system works one must first understand how buffers work.
I hope this. A When any acidic substance enters the bloodstream the bicarbonate ions neutralize the hydronium ions forming carbonic acid and water. In this buffer carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 is the hydrogen ion donor acid and hydrogen carbonate ion HCO 3 is the hydrogen-ion acceptor.
The forearm as an example of a third-class lever. The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer works in a fashion similar to phosphate buffers. Doppler effect in living tissue.
Carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system converts strong bases to a weak base bicarbonate ion and strong acids to a weak acid carbonic acid Phosphate buffer system. A left shift forces more bicarbonate to bind with protons. A buffer is essentially a molecule that has the tendency to either release of bind with hydrogen ions to maintain a pH level 2.
When an acid or. An issue you need to consider is that the pK for H2CO3 is 63. There are a couple of ways to prepare a buffer solution of a specific pH.
The important thing to realize here is that carbonic acid H 2CO3 is actually formed when carbon dioxide CO2 is dissolved in water. The carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system uses the hydrogen ions created by the metabolic and fixed acids to generate carbonic acid which dissociates into H2O and CO2 which can be eliminated by the lungs. Please describe the biochemical processes involving hemoglobin and carbonic acid buffer system when blood pH drops.
The bicarbonate buffering system and titration curves. Question Transcribed Image Text. Catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase carbon dioxide CO 2 reacts with water H 2 O to.
Choose from 180 different sets of carbonic acid bicarbonate buffer system flashcards on Quizlet. The phosphate buffer consists of. The kidneys help control acid-base balance by excreting hydrogen ions and generating bicarbonate that helps maintain blood plasma pH within a normal range.
When sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3 comes into contact with a strong acid such as HCl carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 which is a weak acid and NaCl are formed. A buffer system is a solution that resists change in pH when acids or bases are added to it. The bicarbonate is regulated in the blood by sodium as are the phosphate ions.
Human blood contains a buffer of carbonic acid H 2CO 3 and bicarbonate anion HCO 3 - in order to maintain blood pH between 735 and 745 as a value higher than 78 or lower than 68 can lead to death. In fact this latter aspect of independent regulation is the most powerful aspect of this system. Under normal circumstances there is much more bicarbonate present than carbonic acid the ratio is approximately 201.
Another biological fluid in which a buffer plays an important role in maintaining pH in blood plasma. Production of CO2 leads to an increase in H more acidic removal of CO2 leads to a decrease in H more basic. Carbonic acid Bicarbonate ions Carbon dioxide Hence Carbonic acid bicarbonate buff View the full answer.
A buffer is made up of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. This buffer system can be written as. H 2 CO 3 H 2 O H 3 O HCO 3-.
The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 bicarbonate ion HCO 3 and carbon dioxide CO 2 in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum among other tissues to support proper metabolic function. There are three crucial buffer systems one of which includes the phosphate buffer system in our body to help it contain a proper pH for it to function well. The normal pH range for extracellular.
The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system consists of carbonic acid a weak acid and the bicarbonate anion its conjugate base. After carbon dioxide is dissolved it combines with the water molecules to form carbonic acid. Learn carbonic acid bicarbonate buffer system with free interactive flashcards.
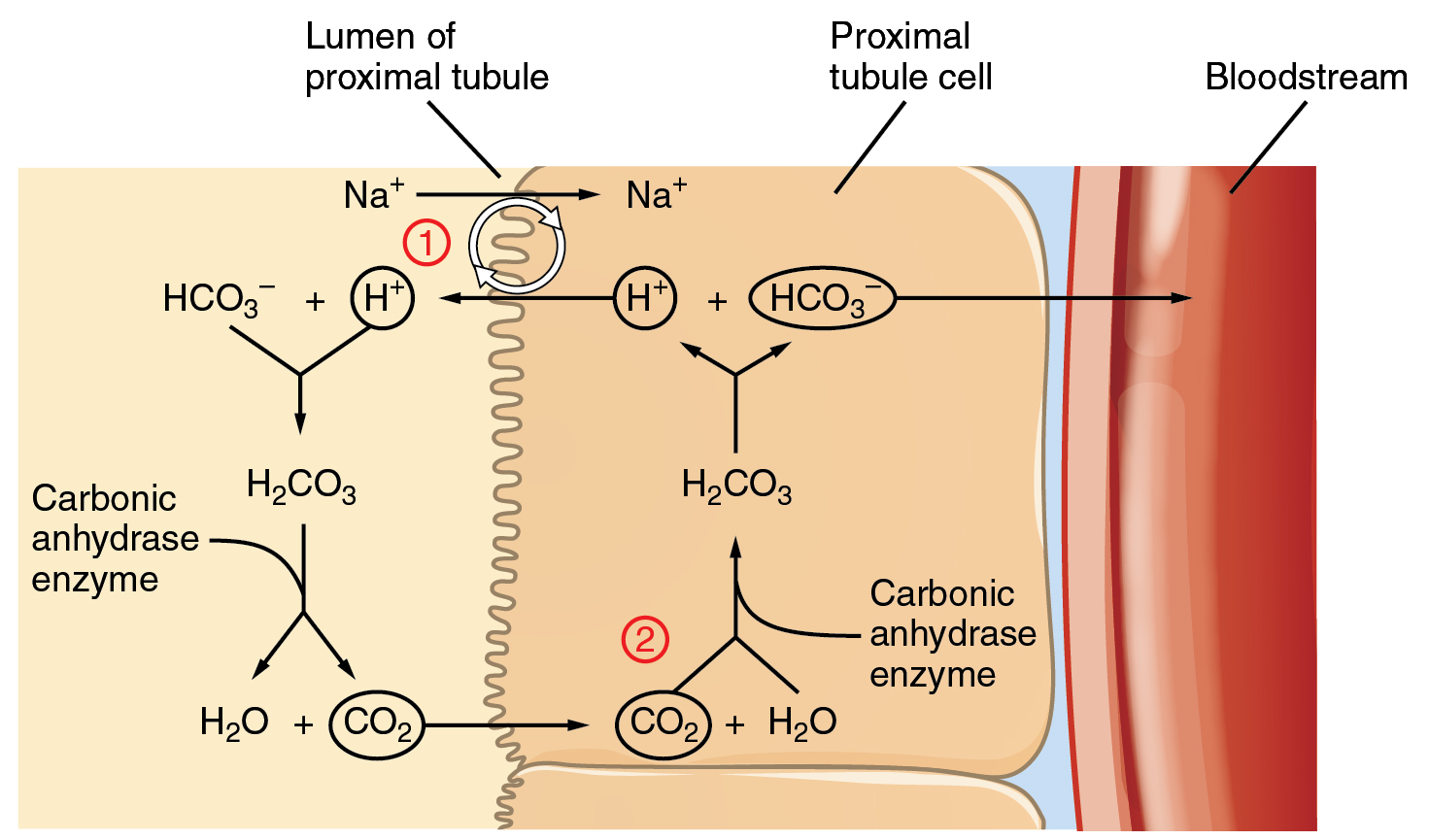
Acid Base Balance Anatomy And Physiology

Solved The Most Important Buffer For Maintaining Blood Acid Base Balance Is The Carbonic Acid Bicarbonate Buffer System The Simultaneous Equilibrium Reaction Of This Biochemical Process Occurs As Shown Below Hzco3 Aq Hz 0 Hz0 Aq

Chemical Buffer Systems And Acid Base Balance

Solved The Bicarbonate Buffer System Is An Effective Physiological Buffer In The Blood Helping Maintain A Normal Physiological Ph Of 7 4 2 Ho Coz G Hcos Aq Ho L H O I Aq

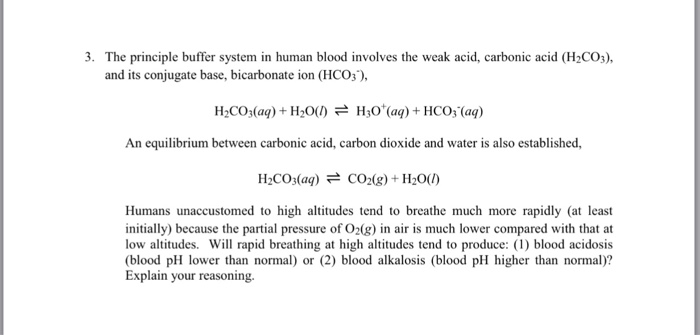
Solved The Principle Buffer System In Human Blood Involves Chegg Com

Understanding The Carbonic Acid Bicarbonate Buffer In Hydroponics Science In Hydroponics

Mcat Question Of The Day The Bicarbonate Buffer System Youtube

Solved Answer The Following Question Regarding A Carbonic Chegg Com
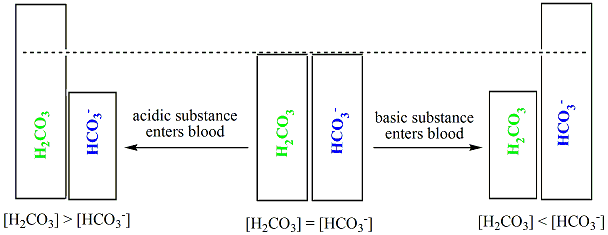
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
How Buffers Help You Periodical 2015
How Buffers Help You Periodical 2015

Solved Blood Is Buffered By The Carbonic Acid Bicarbonate Buffer System Hzco3 Hzo Hco3 Haot If A Relatively Small Amount Of A Strong Acid Were Added To This Buffer Which Component Of The

Bicarbonate Buffer System Flashcards Quizlet

Acids Bases And The H2co3 Hco3 Buffer System Hyperventilation Hypoventilation Youtube
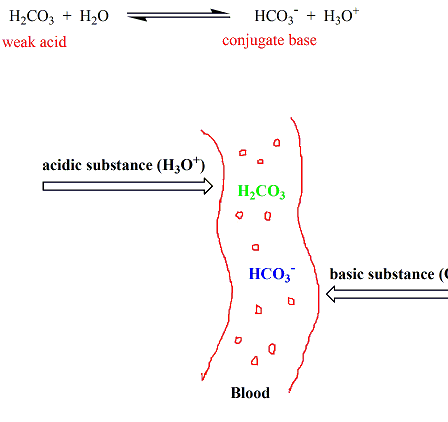
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy

What Is The Carbonic Acid Bicarbonate Buffer System Brainly In



Comments
Post a Comment